Fine motor skills are an essential part of a child’s development, allowing them to perform everyday tasks such as writing, dressing, using utensils, and more. These skills involve the small muscles in the hands, wrists, and fingers, and their refinement is key to helping children grow and achieve independence.
As parents or caregivers, you might notice that your child struggles with tasks like buttoning a shirt or holding a pencil. While some children naturally develop these skills at their own pace, others may benefit from targeted support. Pediatric occupational therapy (OT) focuses on helping children strengthen their fine motor skills, among other areas, so they can navigate daily life more effectively.
We’re going to dive in to the importance of fine motor skills, why occupational therapy is crucial in this area, and provide some expert tips you can try at home to help your child improve their fine motor development.
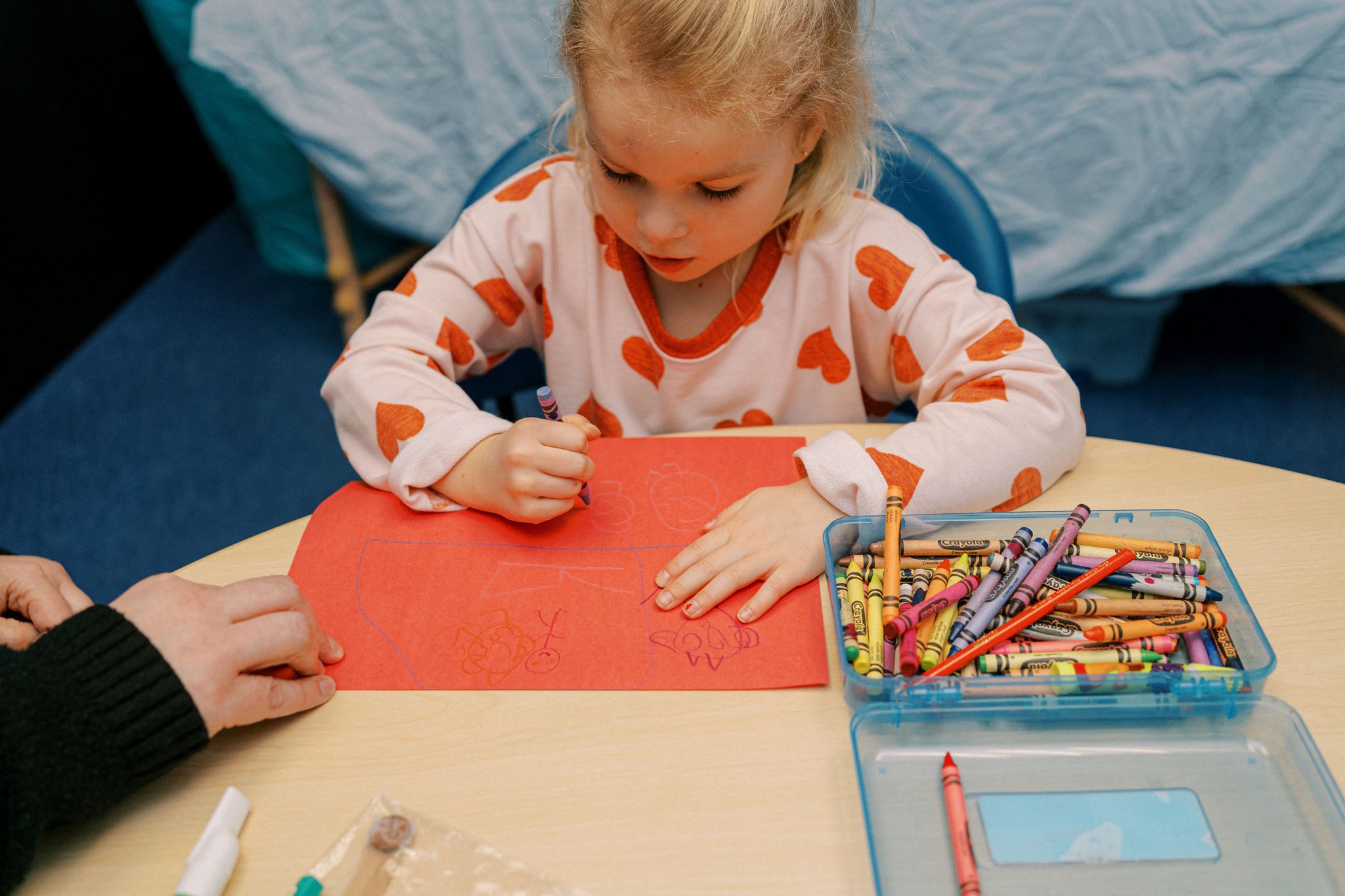

What Are Fine Motor Skills?
Fine motor skills involve the coordination of small muscles, particularly in the hands and fingers, with the eyes. They are essential for performing everyday tasks such as:
- Writing: Holding a pencil, using scissors, drawing shapes
- Dressing: Buttoning clothes, zipping jackets, tying shoelaces
- Self-care: Brushing teeth, feeding yourself with a spoon or fork
- School Activities: Cutting with scissors, gluing objects, handling small items
Without well-developed fine motor skills, children may find it challenging to complete these tasks efficiently. Occupational therapists often work with children to enhance these skills through structured activities designed to promote muscle strength, dexterity, and coordination.
Why Fine Motor Skills Are Crucial for Child Development
Fine motor skills aren’t just about learning to write or hold utensils. They’re a crucial part of a child’s independence and daily functioning. Here’s why these skills are so important:
1. Self-Sufficiency
2. Academic Success
Fine motor skills play a major role in school success. Writing, coloring, and cutting are everyday classroom activities that rely on these skills. Poor fine motor coordination can affect a child’s ability to keep up in school or participate in activities like arts and crafts.
3. Social and Emotional Development
Signs Your Child May Need Help with Fine Motor Skills
It’s important to recognize when your child may need additional support with their fine motor development. Here are some signs to watch for:
- Difficulty holding or using objects such as pencils, scissors, or utensils
- Trouble fastening buttons, zipping zippers, or tying shoelaces
- Avoidance of activities that involve fine motor coordination, such as drawing or cutting
- Difficulty with handwriting or controlling a pencil
- Challenges with feeding themselves, such as using a fork or spoon
If you notice any of these signs, talk to your child’s pediatrician as it may be time to consider occupational therapy in order to help your child improve their fine motor skills.
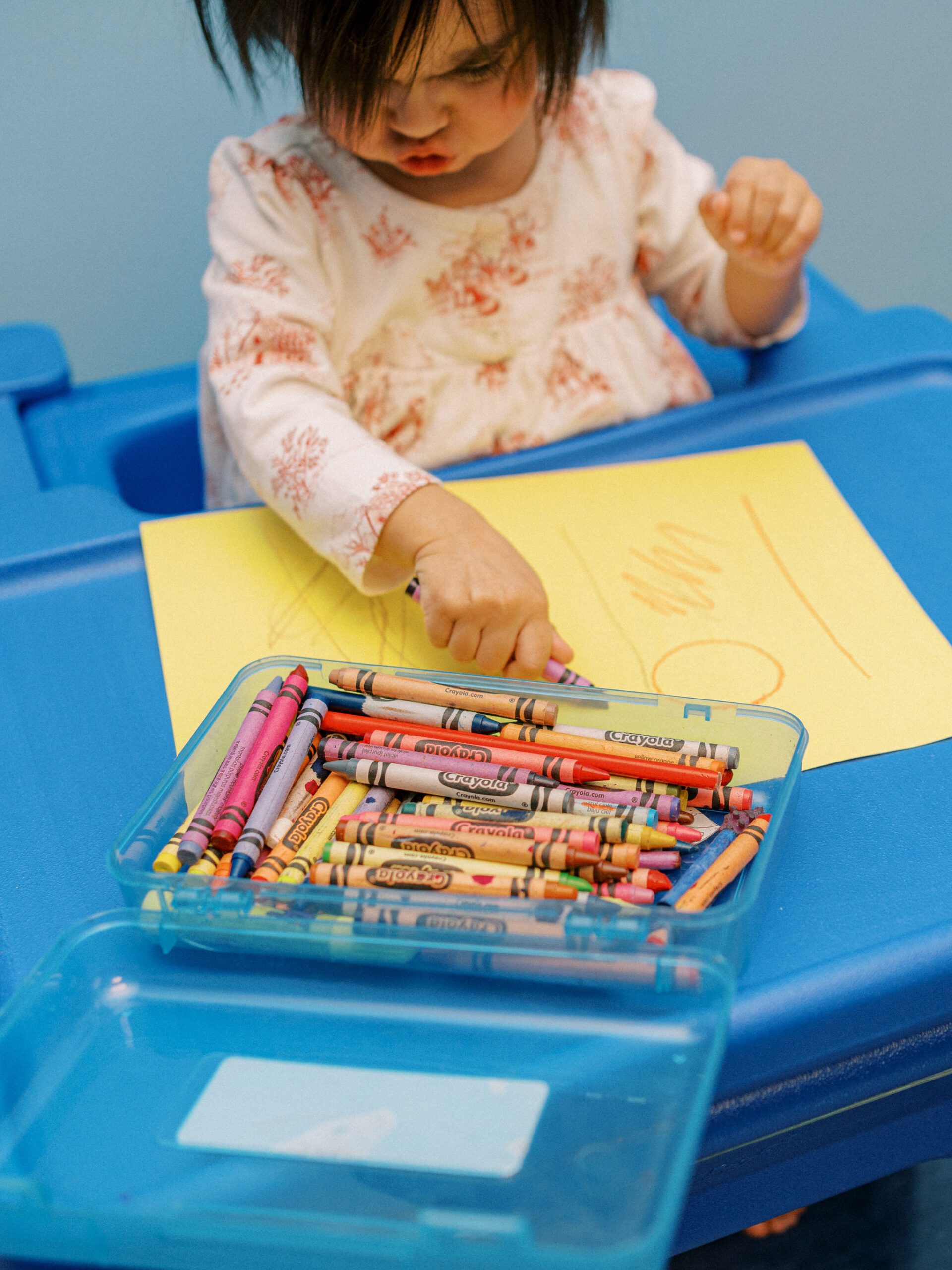

How Pediatric Occupational Therapy Can Help
Pediatric occupational therapists specialize in helping children overcome challenges in fine motor development. They assess each child individually to determine their specific needs and create a customized therapy plan to target their difficulties.
Occupational therapy interventions may include exercises and activities designed to:
- Improve hand strength and dexterity: Therapists use tools such as putty, clothespins, or therapy balls to strengthen hand and finger muscles
- Enhance hand-eye coordination: Activities that require coordination between visual and motor skills, such as threading beads or playing with pegboards, are often used
- Develop fine motor precision: Therapists work with children on tasks that involve precise movements, such as cutting along lines, picking up small objects, or using tweezers
Practical Tips to Improve Fine Motor Skills at Home
Encourage Play with Small Objects
- Activity Idea: Make a bracelet or necklace by stringing beads. Use large, colorful beads and string for your child to practice threading. This builds hand-eye coordination and finger strength. For younger kids, start out using beads and pipe cleaners and work your way up to yarn or string.
- How It Helps: Stringing beads requires precision and coordination, making it a great activity for developing fine motor control.
Use Playdough or Therapy Putty
- Activity Idea: Squeeze, roll, and shape playdough or putty. Have your child make animals or other objects using their hands.
- How It Helps: Playdough is an excellent tool for building hand strength, which is essential for tasks like writing or holding utensils.

Practice Cutting with Child-Safe Scissors
- Activity Idea: Cut along lines or shapes drawn on paper. Start with simple lines and progress to more complex shapes.
- How It Helps: Cutting with scissors strengthens hand muscles and improves hand-eye coordination. Make sure the scissors are age-appropriate and safe for your child to use.
Incorporate Utensil Practice During Mealtime
- Activity Idea: Allow your child to self-feed using a spoon or fork during meals. Offer foods that are easy to scoop, like mashed potatoes or oatmeal.
- How It Helps: Self-feeding encourages hand strength, coordination, and independence.
Play with Pegboards or Puzzles
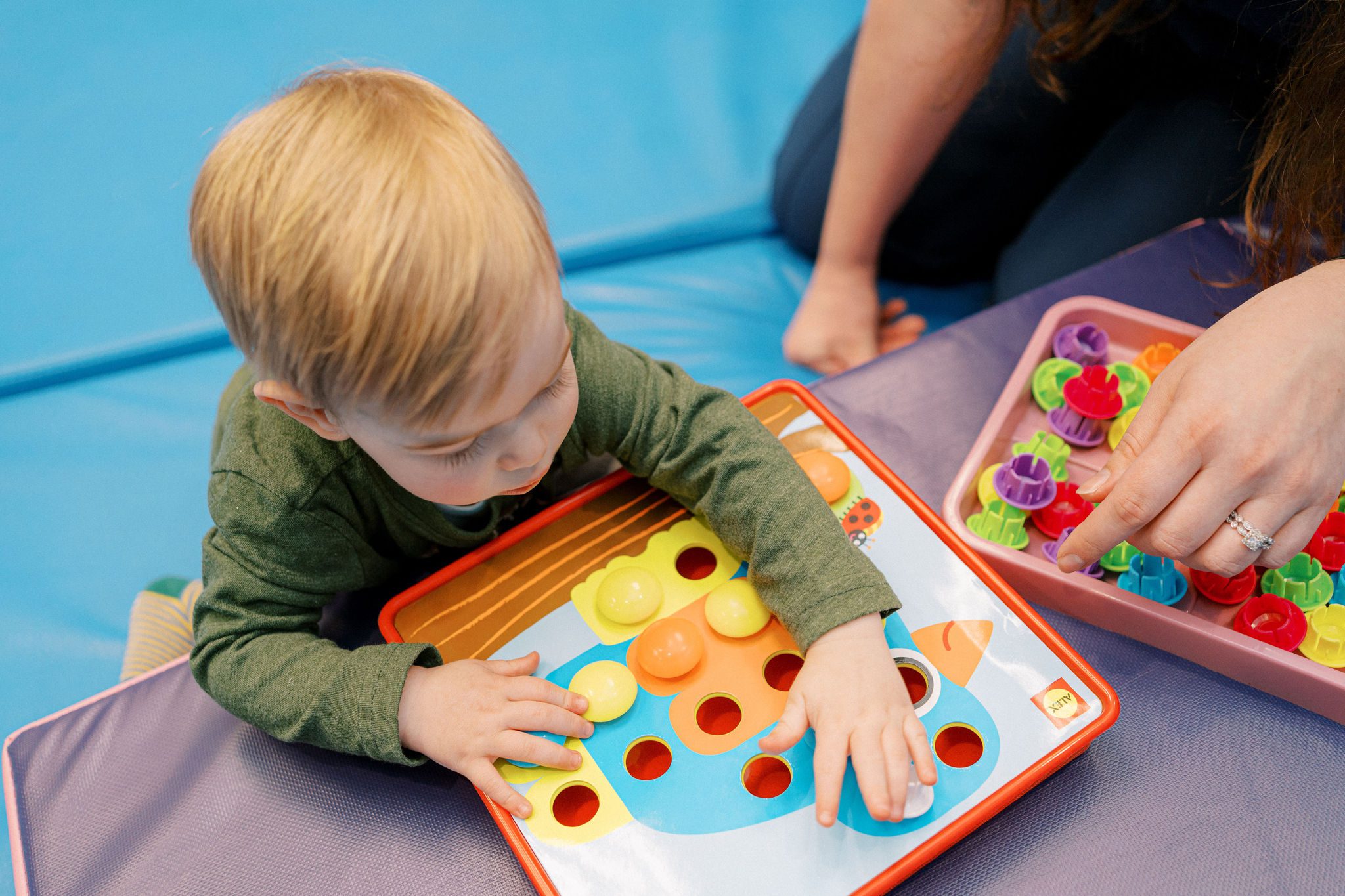
- Activity Idea: Use a pegboard or complete puzzles with small pieces. Encourage your child to place pegs into holes or match puzzle pieces.
- How It Helps: Pegboards and puzzles require fine motor control and precision, making them ideal for developing fine motor skills.

Use Everyday Objects for Fine Motor Practice
- Activity Idea: Button practice. Give your child an old shirt and have them practice buttoning and unbuttoning it. Start with larger buttons and work your way up to smaller buttons which will be more difficult.
- How It Helps: Fastening buttons improves finger strength and dexterity, which are critical for self-dressing.
Introduce Arts and Crafts
- Activity Idea: Drawing, coloring, or using stickers. Encourage your child to create artwork using various tools like crayons, markers, or colored pencils.
- How It Helps: Art activities improve pencil grasp, fine motor precision, and creativity.
Build Hand Strength with Squeezing Activities
- Activity Idea: Use a sponge to transfer water between containers. Your child can squeeze water out of a wet sponge and into another container.
- How It Helps: Squeezing activities strengthen hand and finger muscles, which are vital for writing and using utensils.
When to Seek Professional Help
Final Thoughts on Supporting Fine Motor Development
Fine motor skills are critical for a child’s overall development and independence. By working with a pediatric occupational therapist and incorporating simple activities at home, you can help your child strengthen these skills and improve their ability to navigate everyday tasks.
If you believe your child may need additional support, don’t hesitate to reach out to Michigan Pediatric Therapy. Our team of experienced pediatric occupational therapists can assess your child’s needs and create a customized plan to help them thrive. Contact us today to learn more about how we can assist your child in reaching their full potential.


Michigan Pediatric Therapy
📍 27655 Middlebelt Rd., Suite 130, Farmington Hills, MI 48334
📞 (248) 939-4030
🌐 mipediatrictherapy.com



